Assume the date of the trial balance is March 31. He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com. When a customer fails to repay the amount owed it is known as a bad debt. It is an expense/loss for the business. There is an increase in an asset account (Furniture and Fixtures) in exchange for a decrease in another asset (Cash). Provided services to customers for the amount of $19,000, the customers will pay in 30 days.
Debits and Credits Outline
We will record it by crediting the liability account – Loans Payable. First, we will debit the expense (to increase an expense, you debit it); and then, credit Cash to record the decrease in cash as a result of the payment. A. Record journal entries for the above transactionsB.
Examples of Journal Entries with a PDF
Accounts payable would now have a credit balance of $1,000 ($1,500 initial credit in transaction #5 less $500 debit in the above transaction). The numbers come from the journal entries. Amounts on the left were debits to cash. Amounts on the right were credits to cash. B. Expense accounts are debited when they increase.
Journal Entry for Amortization Expense
13 Purchased $ 240 of supplies on account for use in December. 10 Purchased a new office desk on account, $ 1,050. July 18 Paid for supplies received and already used, $ 2,880. 5 Office space was rented for July, and $ 5,000 was paid for the rental. 10 Collections were made for the services performed on August 6, $ 3,200. 31 Received an order for services at $ 12,000.
Basic Accounting Journal Entries Exercise
Paying later increases a liability which is done with a credit (b). A revenue and expense is not recorded together in the same journal entry. D. Payments are always a decrease to cash which is recorded with a credit. If cash is the credit, the figuring out your form w other account must be a debit. Dividends paid is a decrease to the owner’s equity account retained earnings or dividends paid (either can be used). Dividends paid are not a revenue or an expense and are never recorded on the income statement.
- Actually, we simply transferred the amount from receivable to cash in the above entry.
- Using inventory is recorded as the credit (decreasing) and cost of goods sold is recorded with a debit (expense increasing).
- Purchased manufacturing equipment that cost $39,000.
- 10 Purchased a new office desk on account, $ 1,050.
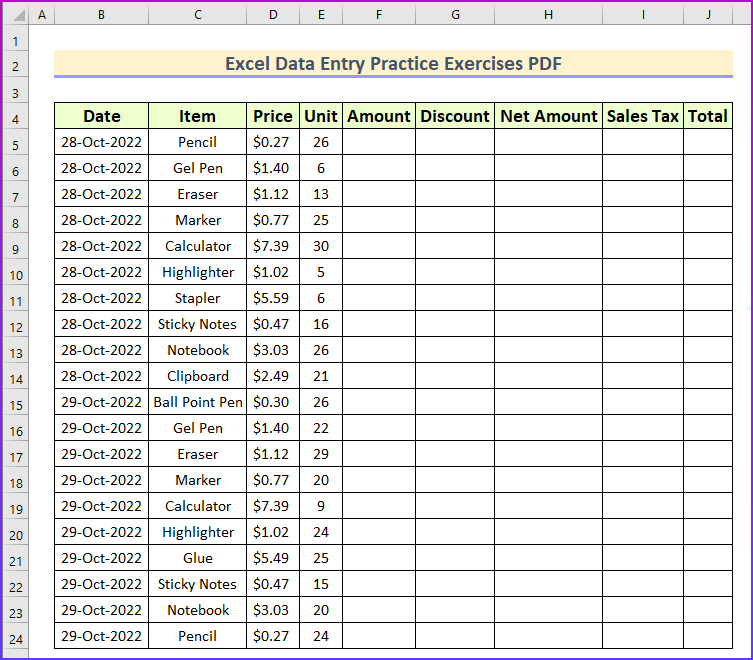
23 Cash collected from customers on account, $ 2,600. 15 Collected cash from customers on account, $ 75,000. 25 Laundry services were performed for customers who paid immediately, $ 22,000. 12 Performed delivery services for customers who promised to pay $ 27,000 at a later date. Exercise G Using your answer for the previous exercise, prepare a trial balance.
13 Cash collections from customers on account, $ 36,000. 6 Purchased delivery trucks for $ 280,000; payment was made by giving cash of $ 150,000 and a 30-day note for the remainder. 23 A note was arranged with the bank for $ 80,000. The cash was received, and a note promising to return the $ 80,000 on 2010 May 30, was signed. 8 Secured an order from a customer for laundry services of $ 7,000.
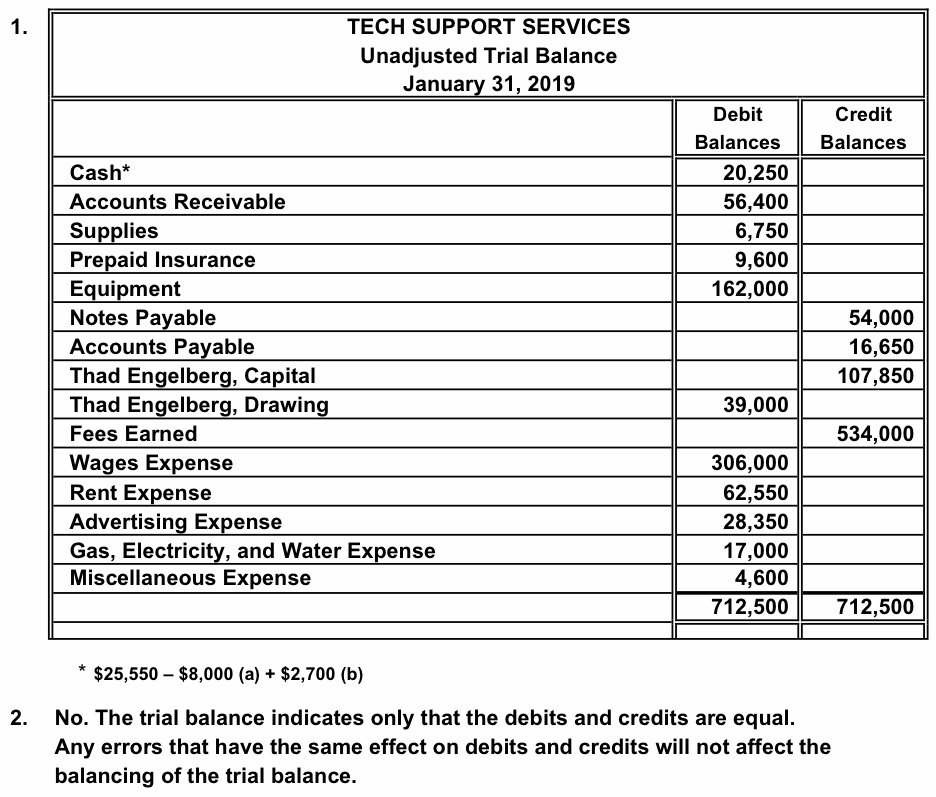
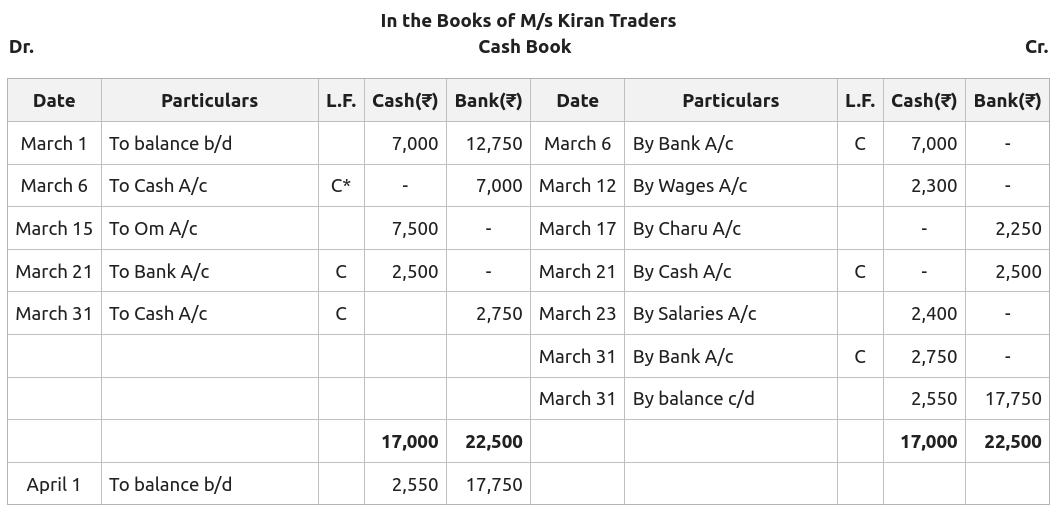
A journal is a book of original entries in which transactions are recorded, as and when they occur. The journal provides data-wise records of all the transactions and the amount of each transaction. Everyday transactions are recorded in a journal chronologically, giving a complete picture of the transaction in one entry. A journal recording is based on a double-entry system so the total of the debit column is equal to the credit column.









Son Yorumlar